简单的例子
在以下示例中,我们将使用设置输入表单value = {this.state.data}。只要输入值发生变化,就可以更新状态。我们正在使用onChange事件,它将监视输入更改并相应地更新状态。
App.jsx
import React from 'react';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
data: 'Initial data...'
}
this.updateState = this.updateState.bind(this);
};
updateState(e) {
this.setState({data: e.target.value});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type = "text" value = {this.state.data}
onChange = {this.updateState} />
<h4>{this.state.data}</h4>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;main.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App.jsx';
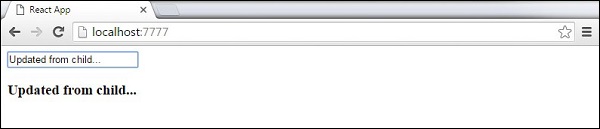
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, document.getElementById('app'));当输入文本值更改时,状态将被更新。
复杂的例子
在下面的示例中,我们将看到如何使用子组件中的表单。onChange方法将触发状态更新,该状态更新将传递到子输入value并呈现在屏幕上。事件一章中使用了类似的示例。每当我们需要从子组件更新状态时,我们都需要将处理update(updateState)的函数作为prop(updateStateProp)传递。
App.jsx
import React from 'react';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
data: 'Initial data...'
}
this.updateState = this.updateState.bind(this);
};
updateState(e) {
this.setState({data: e.target.value});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Content myDataProp = {this.state.data}
updateStateProp = {this.updateState}></Content>
</div>
);
}
}
class Content extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<input type = "text" value = {this.props.myDataProp}
onChange = {this.props.updateStateProp} />
<h3>{this.props.myDataProp}</h3>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;main.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App.jsx';
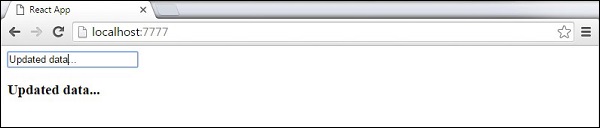
ReactDOM.render(<App/>, document.getElementById('app'));这将产生以下结果。