方法语法(也称为连贯语法)使用Enumerable 或 Queryable静态类中包含的扩展方法,类似于您调用任何类的扩展方法的方式。
编译器在编译时将查询语法转换为方法语法。
以下是LINQ方法语法查询示例,该查询返回字符串集合,其中包含单词“ Tutorials”。
示例:C#中的LINQ方法语法
// 字符串集合
IList<string> stringList = new List<string>() {
"C# Tutorials",
"VB.NET Tutorials",
"Learn C++",
"MVC Tutorials" ,
"Java"
};
// LINQ查询语法
var result = stringList.Where(s => s.Contains("Tutorials"));下图说明了LINQ方法语法的结构。

LINQ方法语法结构
如上图所示,方法语法包括扩展方法和 Lambda 表达式。在枚举(Enumerable)类中定义的扩展方法 Where ()。
如果检查Where扩展方法的签名,就会发现Where方法接受一个 predicate 委托 Func<Student,bool>。这意味着您可以传递任何接受Student对象作为输入参数并返回布尔值的委托函数,如下图所示。lambda表达式用作Where子句中传递的委托。在下一节学习 Lambda 表达式。
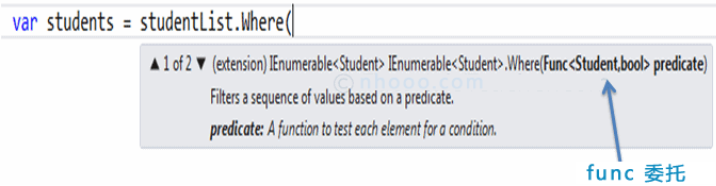
Where 中的 Func 委托
下面的示例演示如何将LINQ方法语法查询与IEnumerable <T>集合一起使用。
示例:C#中的方法语法
// 学生集合
IList<Student> studentList = new List<Student>() {
new Student() { StudentID = 1, StudentName = "John", Age = 13} ,
new Student() { StudentID = 2, StudentName = "Moin", Age = 21 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 3, StudentName = "Bill", Age = 18 } ,
new Student() { StudentID = 4, StudentName = "Ram" , Age = 20} ,
new Student() { StudentID = 5, StudentName = "Ron" , Age = 15 }
};
// LINQ方法语法找出青少年学生
var teenAgerStudents = studentList.Where(s => s.Age > 12 && s.Age < 20)
.ToList<Student>();示例:VB.Net中的方法语法
// 学生集合
Dim studentList = New List(Of Student) From {
New Student() With {.StudentID = 1, .StudentName = "John", .Age = 13},
New Student() With {.StudentID = 2, .StudentName = "Moin", .Age = 21},
New Student() With {.StudentID = 3, .StudentName = "Bill", .Age = 18},
New Student() With {.StudentID = 4, .StudentName = "Ram", .Age = 20},
New Student() With {.StudentID = 5, .StudentName = "Ron", .Age = 15}
}
// LINQ方法语法找出青少年学生
Dim teenAgerStudents As IList(Of Student) = studentList.Where(Function(s) s.Age > 12 And s.Age < 20)
.ToList()要记住的要点
顾名思义,方法语法就像调用扩展方法。
LINQ方法语法又称Fluent语法(连贯语法),因为它允许一系列扩展方法调用。
隐式类型变量-var可用于保存LINQ查询的结果。
